Cocaine is most closely associated with immediate, extreme feelings of euphoria, but its impact reaches much deeper—and can have a catastrophic consequence. It reorders your brain’s pleasure and can impair your brain and nervous system in lasting ways.
Learning about the neurological consequences of cocaine and the impact it can have on your life is an important first step towards awareness, healing, and rehabilitation.
How Cocaine Affects the Brain
The neurological consequences of cocaine can be immediate and powerfully impact your brain, restructuring its delicate balance. It takes over your brain’s complex chemistry, specifically dopamine, responsible for reward and pleasure. What initially seems exciting comes at a high price, opening doors for addiction and long-term brain impairment.1
Dopamine and the Reward System
Cocaine overloads your brain with dopamine, pleasure and reward chemicals and blocks its reuptake. That overexcitation triggers an extreme feeling of ecstasy and euphoria. Over time, however, the process anesthetizes your brain’s reward system, and increasingly larger dosages are needed for the stimulation of pleasure in its absence. That puts many in a trap for addiction, with your brain becoming dependent on cocaine for pleasure.
Acute Neurological Effects
The acute cocaine neurological effects can cause increased alertness, increased vigor, and increased mood. That comes, however, at a high price. Cocaine use can cause extreme repercussions, including seizures, strokes, and acute mental complications such as violent behavior and paranoia. With each use comes a high chance of catastrophic neurological impairment and its consequences becoming a lot deadlier than initially apparent.2
Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex
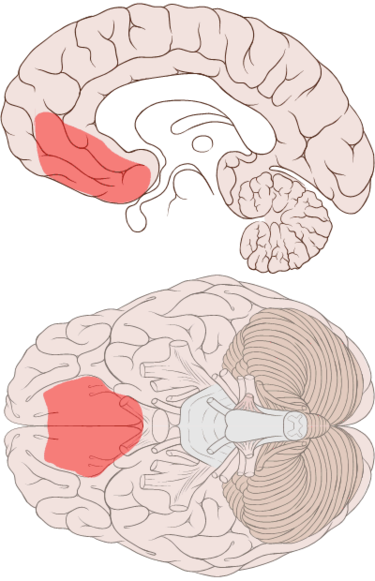
Long-term cocaine use can physically change the brain, reducing gray matter in the ventromedial prefrontal cortex—an area responsible for decision-making and self-control. This can make it harder to resist cravings, manage emotions, and make healthy choices, reinforcing the cycle of addiction.
Long-Term Neurological Damage from Cocaine Use
Using cocaine for an extended period can actually destroy your brain and nervous system. Cocaine use can even impair your memory, thinking, and decision-making.
Long-term use, in addition, creates a high chance of developing mental illnesses such as anxiety and depression. In a few cases, brain damage is irreparable, altering both its function and its appearance.
This proves to show how dangerous it is to use cocaine.
- Cognitive Impairment: Long-term use of cocaine actually destroys your decision-making skills, your ability to pay attention, and your capacity for recalling memories. Cognitive challenges can create problems in your work life and relationships.3
- Mental Health Disorders: The use of cocaine tends to generate extreme mental health complications, like anxiety, depression, and feelings of paranoia. These complications can linger long after you stop using, creating ongoing complications for you in rehab.
- Structural Brain Damage: Long-term use of cocaine generates extreme physical complications in the brain, including loss of gray matter and white matter complications.4
These complications in brain structure have long-term consequences, generating ongoing mental instabilities, reduced mental function, and an inability to build healthy interpersonal relationships.
All these complications illustrate the extreme and long-term neurological consequences of cocaine use.
Get Help for Cocaine Addiction at Cornerstone
Explore residential, outpatient, and virtual pathways to addiction treatment and mental health recovery in Arizona.

The Impact of Cocaine on the Nervous System
In addition to its effects on brain function, cocaine’s impact on the nervous system is equally alarming. It can cause widespread nervous system damage, increasing your vulnerability to severe medical complications.
Nervous System Impacts:
Peripheral neuropathy, causing numbness or pain in extremities
- Increased risk of stroke due to narrowed blood vessels
- Seizures from nervous system overstimulation
- Potential movement disorders resembling Parkinson’s disease
Quick Tip: Prevent Serious Neurological Damage
If you or someone you know is using cocaine, seek help immediately. Stopping early can avert deadly neurological consequences, such as brain damage, and enhance recovery and overall health prospects.
The Role of Early Intervention and Therapy
The neurological effects of cocaine don’t have to be long-term. Addressing the problem early with proper therapy can halt and even reverse a portion of the damage and enable you to regain your life and your happiness in life.
Here are some of the options for treatment:
- Residential Treatment Programs: Around-the-clock care that helps to address both the neurological effects of cocaine use and psychological effects.
- Virtual IOP: Allows you to maintain daily routines while receiving ongoing therapy and support groups and gives you the tools you need to continue healing without changing your routine.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an immediate neurological effect of cocaine use?
An immediate neurological effect of cocaine is the rapid release of dopamine, a brain chemical associated with pleasure and reward. This surge creates an intense feeling of euphoria, increased energy, and heightened alertness. However, it also over-stimulates the nervous system, which can lead to anxiety, restlessness, or even seizures in some cases.
Is long-term use of cocaine a cause of irreparable brain damage?
Yes, Long-term use of cocaine can cause irreparable brain damage, such as cognitive impairment, loss of memory, and brain structure shifts. Aside from the neurological consequences of cocaine use there are also the psychological ones that can linger even after you quit using and make early intervention that much more important..
How does treatment help to reduce neurological effects related to cocaine abuse?
Therapy programs can help to reverse the neurological effects of cocaine and the psychological, through medical care, therapy, and support groups. This helps by addressing both the physical and psychological damage your body has been through due to your cocaine use while also giving you tools to overcome long-term obstacles.
Key Takeaways
- Key Takeaways
- Cocaine use has immediate and long-term neurological effects, including addiction, cognitive decline, and brain damage.
- Understanding these effects is vital to prevent permanent damage and promote recovery.
- Early intervention and treatment are crucial in managing the neurological consequences of cocaine use.
- Comprehensive treatment programs, including residential and virtual options, provide the necessary support to address the complex neurological and psychological impacts of cocaine.
Take Control of Your Recovery Today at Cornerstone
It is important to consider the various neurological effects of cocaine and that although it can cause serious problems, your future doesn’t necessarily have to suffer. With proper care and early intervention, your life can become whole again.
Cornerstone Healing Center offers comprehensive addiction treatment, including specialized care for cocaine addiction. Let us guide you along every step of your journey with a constant reminder that you are NOT alone. Reach out today and start your journey to healing and recovery.