Opioid addiction, a debilitating and often chronic condition, presents a significant challenge to the healthcare industry.
However, there is hope in the form of Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS), a groundbreaking therapy that targets the neural pathways involved in addiction.
DBS is a sophisticated treatment that integrates neuroscience and innovative technology, offering a promising solution to individuals who have yet to succeed with traditional treatment methods.
This article explores DBS’s complexities and potential as a transformative treatment option.
Key takeaways
- Understanding Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS): DBS is a neurosurgical procedure where a device is implanted to send electrical impulses to specific brain areas. It's an innovative approach particularly effective for patients with severe opioid addiction who have not found relief through conventional treatments.
- Mechanism of Action: In the context of opioid addiction, DBS works by targeting brain regions associated with addiction behaviors. This process aims to reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms, thereby aiding in addiction management.
- Suitable Candidates: Ideal candidates for DBS are those with severe, treatment-resistant opioid addiction. A thorough evaluation by medical professionals is essential to determine if DBS is appropriate based on individual health conditions and addiction severity.
- Benefits of DBS: This treatment has shown promise in providing relief from chronic pain without opioids, reducing drug cravings, and improving the quality of life for patients. Research indicates a favorable success rate, making DBS a potential game-changer in addiction therapy.
- Side Effects and Risks: While DBS is generally safe, it can have side effects such as headaches, dizziness, or discomfort at the implant site. Serious side effects like mood or cognitive changes are rare but possible, underlining the need for close medical supervision.
- The DBS Procedure: The process involves deep stimulation brain surgery, which is intricate and requires the implantation of a specialized DBS device. The procedure's complexity highlights the importance of skilled surgical execution and post-operative care.
- DBS Devices: Various advanced DBS devices are available, each with unique features. Technological advancements continue to improve these devices, enhancing treatment efficacy and patient comfort.
- Cost and Accessibility: The cost of DBS can be significant, varying by location and provider. Insurance coverage for DBS is not uniform, necessitating patients to consult with their insurance providers for coverage details.
- Real-World Impact and Success Stories: Deep brain stimulation (DBS) has shown remarkable outcomes for individuals like Gerod Buckhalter by significantly alleviating symptoms of opioid addiction and facilitating a shift toward a more normalized life. These real-life success stories highlight the profound and transformative impact of DBS treatment on patients' lives.
- Future Prospects: The future of DBS in addiction treatment looks promising, with ongoing research and development. However, ethical considerations and long-term implications continue to be areas of active discussion and exploration.
🧠
What is Deep Brain Stimulation? Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is a neurosurgical procedure that involves implanting a device to send electrical impulses to targeted areas of the brain.
Understanding Deep Brain Stimulation
What is Deep Brain Stimulation?
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is an advanced neurosurgical procedure that involves implanting a device, known as a deep brain stimulation device, in the brain to send electrical impulses to targeted areas.1
This treatment modulates neurological activity in precisely identified parts of the brain, often those involved in dysfunctional circuits, such as those seen in various neurological and psychiatric conditions.
In the context of opioid addiction, deep brain stimulation therapy targets regions linked to addiction behaviors and cravings, aiming to restore normal function and provide relief from addiction symptoms.
The process of how deep brain stimulation works is complex.
It involves carefully calibrating the device to tailor the treatment to the individual patient’s needs, making it a highly personalized form of therapy.
The Evolution of Deep Brain Stimulation Therapy
The history of deep brain stimulation therapy traces back several decades, marking a significant evolution in medical science.
Initially, the concept of stimulating the brain to alter neurological functions began with less refined techniques, which, over time, evolved into the more precise and controlled method we know today as deep brain stimulation.
The first uses of deep brain stimulation were focused on treating chronic pain and movement disorders like Parkinson’s disease.
Over the years, the scope of deep brain stimulation treatment has expanded, now encompassing a range of conditions, including severe psychiatric disorders and, more recently, opioid addiction.
This historical context underscores the continuous refinement and expansion of deep brain stimulation as a form of therapy, reflecting both technological advancements and a growing understanding of the brain’s complexities.
🔍
How is Deep Brain Stimulation Used as a Form of Treatment? DBS is a medical treatment that uses implanted devices to regulate abnormal neural activity. It is commonly used for Parkinson’s disease and severe psychiatric conditions, including treatment-resistant opioid addiction. DBS modulates the brain circuits involved in addictive behaviors, providing a new treatment option for patients where traditional therapies have failed.
Deep Brain Stimulation as a Form of Treatment
Deep brain stimulation stands out as a neurosurgical treatment that uniquely intersects the realms of neurology and cutting-edge technology.
Unlike traditional surgery that removes or alters brain tissue, deep brain stimulation involves implanting a device that modulates neural activity without causing structural changes.
This deep-stimulation brain surgery is performed with the utmost precision, targeting specific brain areas responsible for treating the condition’s symptoms.
The procedure involves placing electrodes in targeted brain regions and connecting them to a pulse generator, usually implanted under the skin in the chest.
The generator sends controlled electrical impulses to the brain, which can be adjusted or turned off without additional surgery, making it a versatile and reversible form of treatment.
Broad Applications of Deep Brain Stimulation Therapy
While the use of deep brain stimulation therapy in treating opioid addiction is a significant advancement, its applications extend far beyond.
Initially developed to manage chronic pain, deep brain stimulation has become a primary treatment for a range of movement disorders, most notably Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor, and dystonia.
Its success in these areas has led to explorations into psychiatric disorders, such as major depression and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
The flexibility of deep brain stimulation in targeting different brain areas makes it a promising therapeutic avenue for various conditions that have proven resistant to conventional treatments.
This breadth of application highlights the transformative potential of deep brain stimulation therapy in modern medicine, offering hope and improved quality of life to patients with diverse neurological and psychiatric disorders.
👨⚕️
What does the procedure of Deep Brain Stimulation surgery involve? DBS surgery implants a device that delivers electrical impulses to specific brain regions. Electrodes are placed in the brain and connected to a pulse generator in the chest. The generator sends controlled signals to modulate neural activity, treating conditions like opioid addiction.
The Procedure of Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery
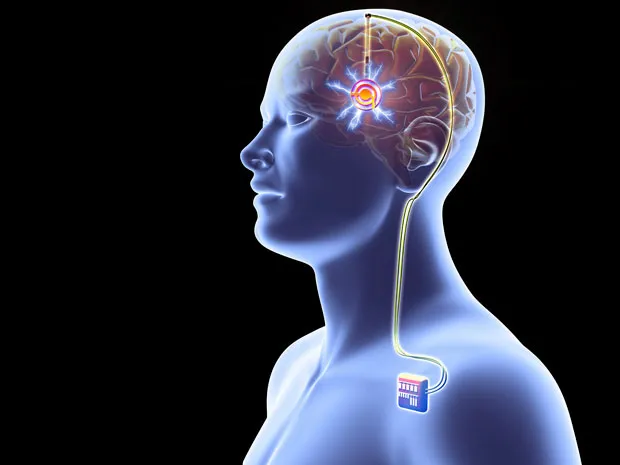
Deep stimulation brain surgery, a critical component of deep brain stimulation treatment, is a meticulously orchestrated procedure that unfolds in several key steps.
Initially, a thorough pre-operative evaluation is conducted to map the brain and identify the precise target areas for electrode placement.
Under general anesthesia, a small hole is drilled in the skull, and a thin electrode is carefully inserted into the brain, targeting specific areas identified as responsible for the symptoms.2
Intraoperative testing may be performed to ensure optimal placement.
The electrode is then connected to a pulse generator, typically implanted under the skin in the chest or abdomen.
Post-surgery, patients undergo a recovery period followed by programming sessions where the deep brain stimulation device is calibrated to deliver the most effective stimulation for the patient’s specific condition.
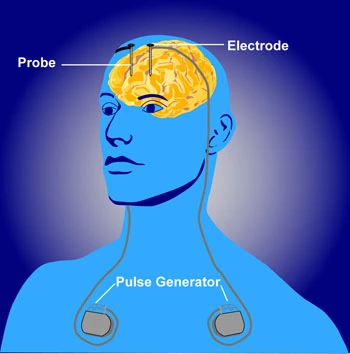
The Role and Design of the Deep Brain Stimulation Device
The deep brain stimulation device plays a pivotal role in the efficacy of deep brain stimulation therapy.
The device consists primarily of three components:
• The lead (a thin, insulated wire with electrodes at the end).
• The extension (a wire connecting the lead to the pulse generator).
• The pulse generator itself (a battery-powered device that creates the electrical impulses).
The device’s design is sophisticated yet patient-centric, minimizing discomfort while maximizing therapeutic benefits.
The pulse generator’s settings are programmable and adjustable, allowing healthcare providers to fine-tune the electrical impulses in strength, frequency, and duration to suit individual patient needs.
Deep brain stimulation therapy is highly versatile as it can adapt to the changing needs of patients, whether it is for movement disorders or complex conditions such as opioid addiction.
This customization capability is paramount in achieving the best possible outcomes for patients.
Technological Advancements in Deep Brain Stimulation Devices
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) has seen significant technological advancements to improve patient outcomes and usability.
Innovations include rechargeable battery systems, which extend the device’s lifespan and reduce the need for replacement surgeries.
There are also developments in directional leads that allow for more precise targeting of brain areas, potentially reducing side effects and improving efficacy.
Wireless programming capabilities have been enhanced, enabling easier adjustments to stimulation settings and better patient monitoring.
Additionally, some of the latest devices are MRI-compatible, allowing patients to undergo MRI scans safely.
These advancements represent a significant leap forward in the personalization and effectiveness of DBS therapy.
💊
How Does Deep Brain Stimulation Work for Treating Opioid Addiction? DBS treats opioid addiction by implanting a device that sends electrical impulses to targeted areas of the brain involved in addiction, such as the nucleus accumbens. This modulation of brain activity can reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms, aiding in recovery.
Deep Brain Stimulation for Opioid Addiction
Targeting Opioid Addiction with Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep brain stimulation treatment offers a novel approach to combating opioid addiction, a condition notoriously challenging to treat.
This advanced therapy specifically targets brain regions implicated in the cycle of addiction, such as the nucleus accumbens and other areas associated with reward and pleasure.3
By delivering targeted electrical impulses to these areas, deep brain stimulation aims to modulate the neural circuits that drive addictive behaviors.
This intervention can potentially reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms, key hurdles in overcoming opioid addiction.
The precision of deep brain stimulation therapy allows for a targeted approach, making it a significant tool in the arsenal against severe opioid dependency, especially in cases where other treatments have failed.
This innovative approach highlights the potential of deep brain stimulation in rewriting the narrative of addiction treatment, providing hope for sustained recovery and improved quality of life.
🔍
What is the Success Rate of Deep Brain Stimulation in Treating Opioid Addiction? DBS has a promising success rate in treating opioid addiction. Early studies show significant reductions in cravings and relapse rates, but its long-term efficacy and outcomes are still under investigation. Further research is needed to establish its broader effectiveness.
Benefits and Success Rate
Comprehensive Benefits of Deep Brain Stimulation
The benefits of deep brain stimulation extend far beyond its primary application in movement disorders, showcasing remarkable potential in the realm of addiction treatment.
Deep brain stimulation therapy offers hope for patients suffering from severe opioid addiction when other treatments have failed.
Key benefits include a significant reduction in drug cravings and withdrawal symptoms, which are significant barriers to recovery.
Additionally, deep brain stimulation can improve overall mood and quality of life, as it targets the neural pathways associated with addiction and emotional regulation.
For many, this translates into a more remarkable ability to engage in rehabilitation programs and a lower risk of relapse.
The non-destructive nature of the treatment and its reversibility also contribute to its appeal, offering a safer alternative than more invasive procedures.
Success Rate of Deep Brain Stimulation in Treating Opioid Addiction
When it comes to the success rate of deep brain stimulation in treating opioid addiction, the landscape is promising yet continuously evolving.
Early clinical studies and trials have shown encouraging results, with many patients experiencing a substantial reduction in addiction symptoms and an improved ability to abstain from opioid use.
However, it’s important to note that deep brain stimulation is still relatively new in the context of treating opioid addiction, and long-term success rates are still being studied.
The success of deep brain stimulation treatment varies from patient to patient.
It is heavily influenced by factors such as the severity of addiction, the specific brain regions targeted, and the individual’s overall health and lifestyle.
Despite these variables, deep brain stimulation stands as a groundbreaking option, potentially revolutionizing the way severe opioid addiction is treated and offering a new lease on life for those who have exhausted other avenues of treatment.
😵
Are There Any Side Effects Associated with Deep Brain Stimulation? Like any medical procedure, deep brain stimulation can have side effects. These may include headaches, dizziness, and discomfort at the implantation site. Rarely, more serious side effects like changes in mood or cognition can occur. It’s important for deep brain stimulation patients to be closely monitored by their healthcare team.
Risks and Side Effects
Exploring the Side Effects of Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) therapy, while transformative for many, comes with its potential side effects and risks, ranging from transient to more enduring.
Patients might experience temporary symptoms such as headache, nausea, and discomfort around the implantation sites immediately following the procedure.
More infrequent but serious side effects include neurological changes, such as mood, cognition, or speech alterations, and, in rare cases, infection or bleeding within the brain.
These risks underscore the importance of a thorough pre-surgical evaluation and ongoing post-operative monitoring to effectively manage and mitigate potential side effects.
Addressing Concerns About Scarring From Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery
The surgical aspect of deep brain stimulation involves making small incisions in the scalp to implant the electrodes and in the chest area for the pulse generator, which can lead to concerns about scarring.
Modern surgical techniques aim to minimize the visibility of scars, and the incisions are typically small, leading to less noticeable scarring.
Post-operative care includes strategies for scar care and management, helping to reduce their appearance over time.
Patients need to discuss any concerns about scarring with their surgical team to understand what to expect and how to care for their incisions after the procedure.
👍
Who is Considered a Good Candidate for Deep Brain Stimulation Therapy? A good candidate for deep brain stimulation therapy is typically someone who has severe opioid addiction and has not responded to traditional treatments. Patients should be thoroughly evaluated by medical professionals to determine if DBS is a suitable option based on their health condition and addiction severity.
The Ideal Deep Brain Stimulation Patient
Criteria for a Good Deep Brain Stimulation Candidate
Identifying Ideal Candidates for Deep Brain Stimulation:
The ideal deep brain stimulation patient often grapples with severe, treatment-resistant conditions where conventional therapies have failed.
For those considering deep brain stimulation for opioid addiction, key criteria include a documented history of addiction severity, unsuccessful outcomes with standard treatments such as medication and psychotherapy, and a stable psychological condition to withstand the rigors of DBS therapy.
Medical professionals perform comprehensive evaluations to ensure potential candidates can safely undergo the procedure and are likely to benefit from its application.
Case Studies of Deep Brain Stimulation Patients
Deep Brain Stimulation Patient Success Stories
While individual results vary, several case studies highlight the transformative potential of deep brain stimulation for patients with otherwise intractable conditions.
One notable example involves patients with Parkinson’s disease experiencing significant improvements in motor function and quality of life post-DBS.
In the realm of addiction, preliminary case studies, such as individuals with severe opioid addiction undergoing DBS, show promising outcomes in reducing cravings and enabling recovery paths not previously possible.
The Journey of Gerod Buckhalter: Overcoming Addiction with Deep Brain Stimulation
Gerod Buckhalter’s two-decade battle with opioid addiction led him to become the first participant in a pioneering clinical trial at West Virginia University, exploring Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) for addiction.4
Funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse, this innovative trial marked a significant advancement.
Remarkably, Buckhalter has remained drug-free for over 600 days post-surgery, showcasing DBS’s potential in addiction treatment.
This breakthrough exceeded expectations and positioned Buckhalter’s case as a milestone in addiction therapy research in the U.S.
💰
How Much Does Deep Brain Stimulation Treatment Cost and is it Covered by Insurance? The cost of deep brain stimulation treatment can vary significantly depending on the healthcare provider and region. It’s a sophisticated procedure involving surgery and specialized equipment. Insurance coverage for DBS varies; patients should consult with their insurance providers to understand the extent of coverage and potential out-of-pocket costs.
Cost and Accessibility
Evaluating the Cost of Deep Brain Stimulation
The cost of deep brain stimulation (DBS) can be substantial, encompassing the surgical procedure, the device itself, and ongoing care and adjustments.
Prices vary widely depending on geographic location, healthcare provider, and the patient’s specific needs.
The complexity of the surgery and the technology involved contribute to the overall expense.
Patients considering DBS should prepare for a significant investment in their health, but the potential benefits in quality of life and symptom management often justify the cost.
Navigating Insurance and Accessibility for DBS Treatment
The accessibility of deep brain stimulation therapy largely depends on insurance coverage, which can vary significantly between policies and providers.
While many insurance companies cover DBS for approved conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, coverage for emerging applications like addiction treatment may be less straightforward.
Patients should engage with their insurance providers early in decision-making to understand their coverage, potential out-of-pocket costs, and any necessary pre-approvals.
Advocacy and negotiation by healthcare providers can also be crucial in securing coverage for this life-changing therapy.
Future of Deep Brain Stimulation in Addiction Treatment
Future Developments in DBS for Addiction Treatment
As we venture into the future, the potential of deep brain stimulation (DBS) in addiction treatment shines brighter with each advancement.
Research is focused on refining the precision of electrode placement for targeted therapy and enhancing the overall design and functionality of DBS devices for improved patient experience.
The exploration into DBS’s applicability across a wider spectrum of addictive behaviors promises a new era of personalized medicine, aiming to tailor treatments to individual needs and conditions.
This focus on innovation holds the promise of transforming addiction therapy, making it more effective and adaptable to various types of substance dependencies.
Ethical and Long-term Considerations in DBS
The evolution of deep brain stimulation therapy brings to the forefront critical ethical and long-term considerations that must be navigated with care.
As we explore the capabilities of DBS, questions arise regarding informed consent, patient selection criteria, and the ethical implications of potential personality and behavioral changes, which become increasingly complex.
The exploration of DBS’s long-term impact on neurological and psychological health is essential, as is understanding its broader societal implications.
Balancing these ethical considerations with the undeniable benefits of DBS is crucial in guiding the responsible advancement of this technology, ensuring it serves the best interests of patients and society alike.
Deep Brain Stimulation's Role in Overcoming Opioid Addiction
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a new and important treatment for severe opioid addiction.
It offers hope where traditional methods have failed.
This innovative approach targets the neural pathways in the brain and has promising results in reducing cravings and assisting with recovery.
However, this is just the beginning.
Ongoing research and increased awareness are needed to realize the full potential of DBS, making it more accessible and effective.
The future looks bright for those who struggle with addiction, with DBS leading the way in transforming lives.



