How Long Does Alcohol Stay In Your System?
Understanding Alcohol Breakdown
When alcohol enters the body, it is rapidly absorbed by the stomach and small intestine. From there, it travels to the bloodstream and reaches various organs. The liver plays a pivotal role in breaking down alcohol, a process known as metabolism. Most alcohol metabolism happens in the liver, where enzymes like alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) convert alcohol into other chemicals, which are then further processed and eliminated from the body. The human body absorbs alcohol quickly from the stomach and small intestine, with the liver being the primary site for its metabolism. This process is essential for reducing alcohol levels in the blood.1Average Metabolism Rate
The rate at which the body metabolizes alcohol can vary significantly from person to person. This rate is usually measured in terms of how many grams of ethanol are metabolized per kilogram of body weight per hour. Factors that can influence this rate include the amount of alcohol consumed, individual drinking habits, food in the stomach, and genetic differences in liver enzymes. The rate of ethanol elimination from the body is not constant and can be influenced by various factors, including the volume of alcohol intake, individual drinking patterns, and food consumption.2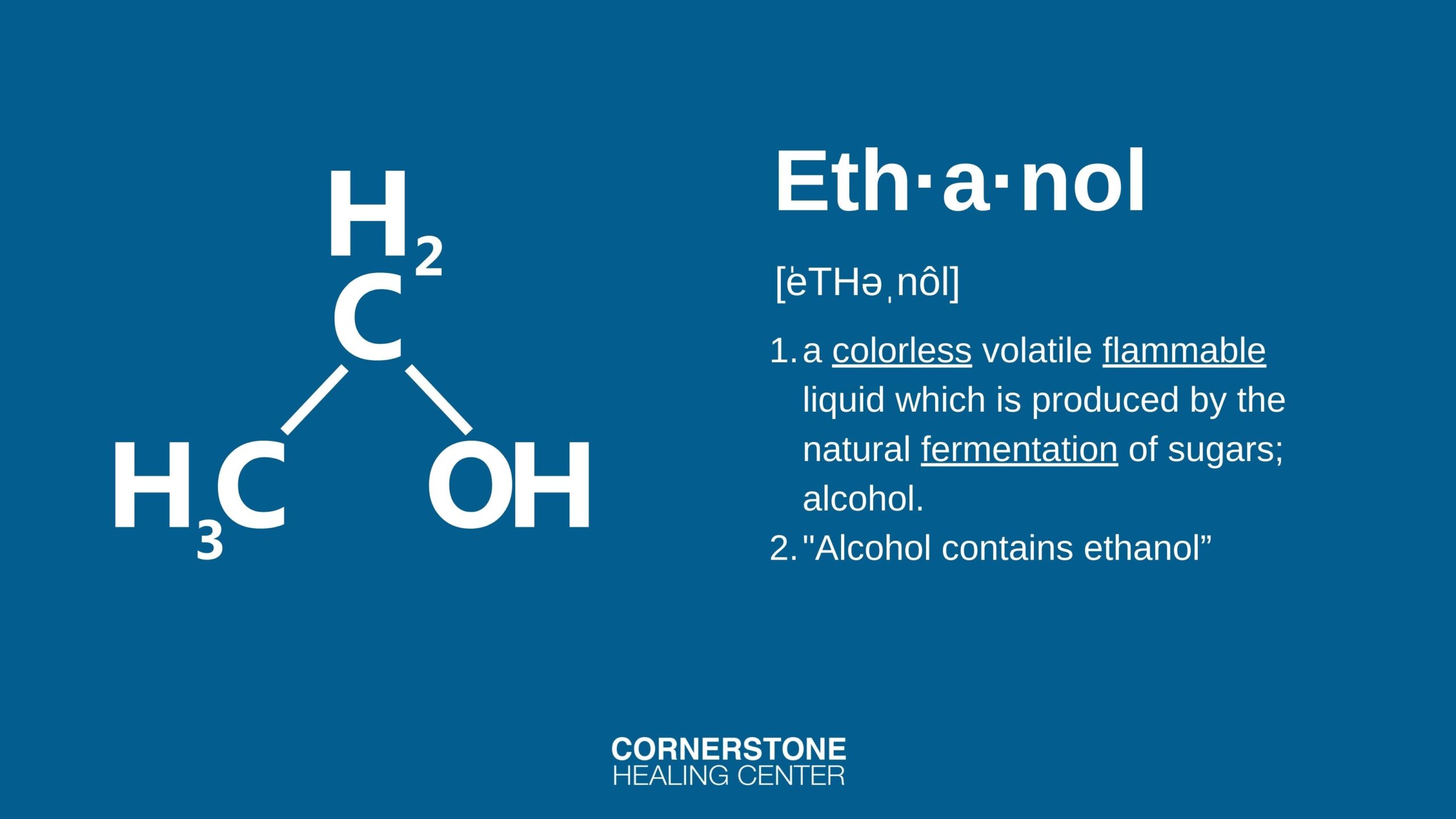
🔑 Key takeaways
- Alcohol is absorbed quickly and metabolized mostly in the liver, with metabolism rates varying due to individual factors like diet and gender.
- BAC is eliminated through liver metabolism and can stay in blood up to 6 hours and in urine up to 48 hours.
- Misconceptions exist around quick sobering up, and moderate drinking can significantly impact physiological responses.
- Knowledge of alcohol's duration in the body is important for health and legal considerations, highlighting responsible drinking.
Factors Influencing Alcohol Metabolism
Biological Factors
Age and gender play a significant role in how the body metabolizes alcohol.
Studies show that there are noticeable differences in alcohol pharmacokinetics between men and women, partly due to hormonal variations.
For instance, estrogen can affect the activity of enzymes involved in alcohol metabolism, potentially causing women to metabolize alcohol at a different rate compared to men.
Gender differences in alcohol metabolism are evident, with research suggesting that women may break down alcohol faster than men due to hormonal differences.3
Dietary Influence
The presence or absence of food in the stomach significantly affects how alcohol is absorbed into the bloodstream.
Eating before or while drinking can slow down the absorption of alcohol, leading to lower peak blood alcohol concentrations.
This is because food competes with alcohol for absorption in the small intestine and can also stimulate increased enzyme activity in the liver, aiding in faster alcohol metabolism.
Food intake plays a vital role in alcohol absorption and metabolism, significantly influencing blood alcohol levels and the rate at which alcohol is cleared from the system.4
💡
How long does alcohol stay in your blood?
Alcohol generally remains in the bloodstream for up to 6 hours. However, this duration can vary based on individual metabolism rates, the amount of alcohol consumed, body weight, and whether the person has eaten. It’s important to note that effects on coordination, judgment, and reaction time can last longer than the alcohol itself.
Alcohol in the Bloodstream
Blood Alcohol Concentration Explained
Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) is a measure of the amount of alcohol in your bloodstream. The rate at which alcohol is eliminated from the bloodstream, or the BAC elimination rate, is primarily through oxidative metabolism in the liver.
This process breaks down alcohol into acetic acid before it is finally eliminated from the body.
The rate of elimination can vary significantly based on several factors, including individual drinking habits, the amount of alcohol consumed, and whether a person has eaten.
The elimination of alcohol from the bloodstream involves complex metabolic processes in the liver, with varying rates influenced by factors such as consumption patterns and fasting status.5
Legal and Health Implications
The measurement of BAC is essential for legal and health purposes.
In many jurisdictions, a BAC of 0.08% is the legal threshold for impaired driving.
BAC levels are typically measured using breathalyzers or blood tests.
These measurements help in enforcing driving under the influence (DUI) laws and also serve as an indicator of potential alcohol-related health risks.
Exceeding legal BAC limits can lead to legal consequences, including fines, license suspension, and imprisonment.
🍺
How long does alcohol stay in your urine?
The detection of alcohol in urine can vary, but typically, it can be identified for up to 48 hours after consumption. This duration depends on several factors, such as the quantity of alcohol consumed and the individual’s metabolic rate. In cases of heavy drinking, more sensitive tests like EtG urine tests can detect alcohol for a longer period, possibly up to 3-5 days.
Alcohol in the Urinary System
Urinary Detection of Alcohol
The journey of alcohol into the urinary system begins with its consumption and subsequent absorption into the bloodstream. From there, it’s metabolized predominantly in the liver.
The byproducts of this metabolism, including alcohol, are then filtered by the kidneys and excreted through urine.
This process starts relatively quickly after alcohol consumption and is the basis for urine tests that detect alcohol or its metabolites.
Variability Factors
Several factors influence the duration of alcohol detection or its metabolites in urine. These include the amount of alcohol consumed, the individual rate of alcohol metabolism, and their hydration status.
For example, a higher alcohol intake or slower metabolic rate can extend the detection window. Additionally, hydration levels can dilute the alcohol concentration in the urine, potentially affecting the outcome of urine tests.
The sensitivity of the testing method also plays a crucial role; more sensitive tests can detect trace amounts of alcohol or its metabolites even several days after consumption.
Elimination of Alcohol from the Body
Role of Kidneys in Alcohol Elimination
The kidneys play a vital role in eliminating alcohol from the body. Once alcohol is absorbed and metabolized, the liver converts it into water-soluble substances that are easier for the kidneys to process.
The kidneys then filter these substances from the blood and excrete them through urine.
This process is part of the body’s natural detoxification system, working to clear alcohol and its byproducts from the system and maintaining a balance of fluids and electrolytes.
It’s important to note that the kidneys’ efficiency in eliminating alcohol can vary based on individual health, age, and the overall functioning of the urinary system.
The kidneys’ role in this process highlights the interconnected nature of the body’s systems in managing and eliminating substances like alcohol.
Misconceptions and Safe Practices
A common misconception about alcohol is the idea of ‘sobering up’ quickly. Many believe that certain actions like taking a cold shower, drinking coffee, or getting fresh air can speed up the elimination of alcohol from the body.
However, these methods do not hasten the metabolic process. The only thing that lowers Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) over time is the body’s natural metabolic process.
Practicing safe drinking habits, understanding one’s limits, and allowing sufficient time for alcohol to metabolize are crucial for safety and health.

Impact of Alcohol on Health
Short-Term Effects
The short-term effects of alcohol consumption can vary but often include changes in coordination, mood, and cognitive functions. People may experience decreased inhibitions, impaired judgment, and slower reaction times.
Physiologically, alcohol can affect the central nervous system, leading to symptoms like slurred speech and unsteady movement.
Moderate alcohol consumption can increase heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen consumption, and blood lactic acid during exercise in women. 6
Long-Term Health Implications
Regular, long-term alcohol use can have significant health implications. Chronic drinking can lead to the development of various diseases and disorders, including liver disease, cardiovascular problems, and neurological complications.
It can also increase the risk of certain cancers, impact mental health, and contribute to social and relationship problems.
It’s important to understand these potential long-term consequences to make informed decisions about alcohol consumption.
Get Support for Alcoholism
Responsible alcohol consumption is key to maintaining health and safety. Excessive drinking can lead to serious health risks and impair judgment and coordination.
It’s essential to be aware of how much and how often you drink and to recognize the signs of problematic drinking.
If you have concerns about your alcohol consumption or its effects on your health, we encourage you to seek professional advice.
At Cornerstone Healing Center, we offer comprehensive care and support for individuals struggling with alcohol use.
Remember, seeking help is a sign of strength and the first step towards better health and well-being.
Understanding the effects of alcohol on your body and mind is essential when making choices about drinking. Stay aware, stay informed, and don’t hesitate to seek help when needed.