Dilated pupils, medically known as Mydriasis, can result from various factors, including certain drugs that impact the nervous system. This article will explore dilated pupils and provide an overview of the drugs that can lead to this condition.
Understanding Dilated Pupils (Mydriasis)
Drugs That Can Cause Pupil Dilation
Various drugs can cause pupil dilation due to their effects on the nervous system. These substances typically belong to categories like stimulants, hallucinogens, and anticholinergic drugs. In some cases, pupil dilation is an unintended side effect resulting from a drug’s impact on the body’s physiological systems.
Let’s look at the various drugs known to cause dilated pupils.
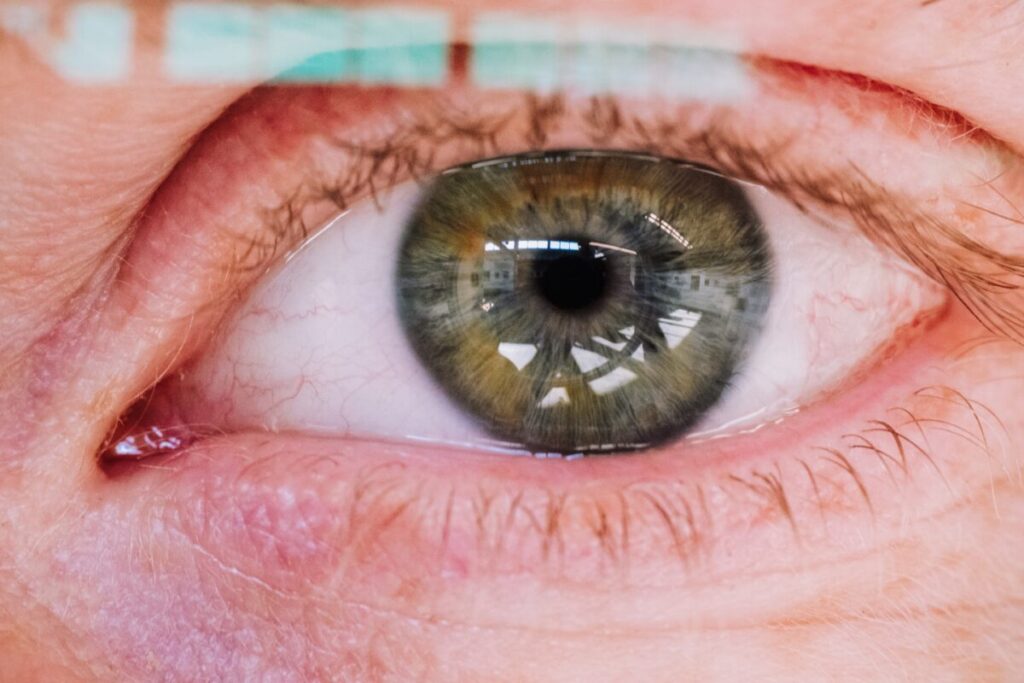

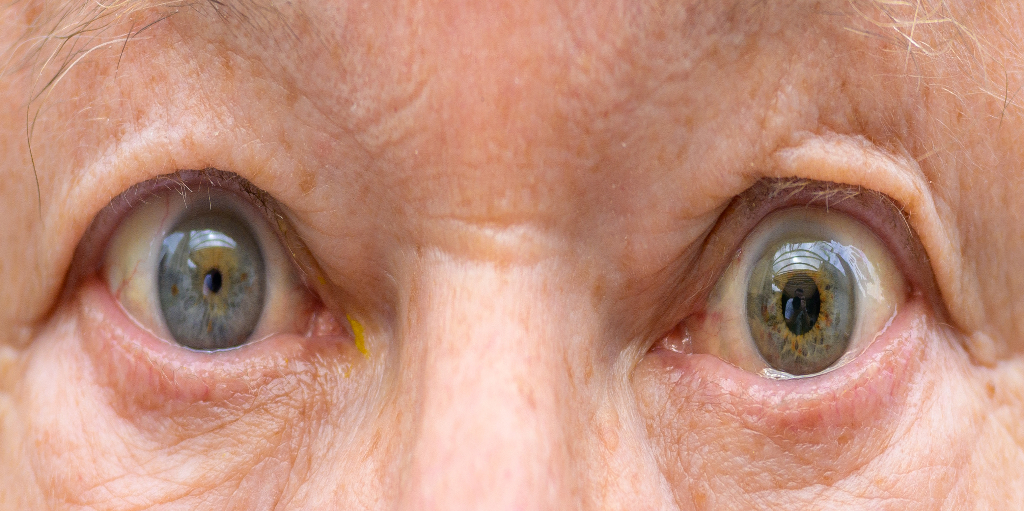
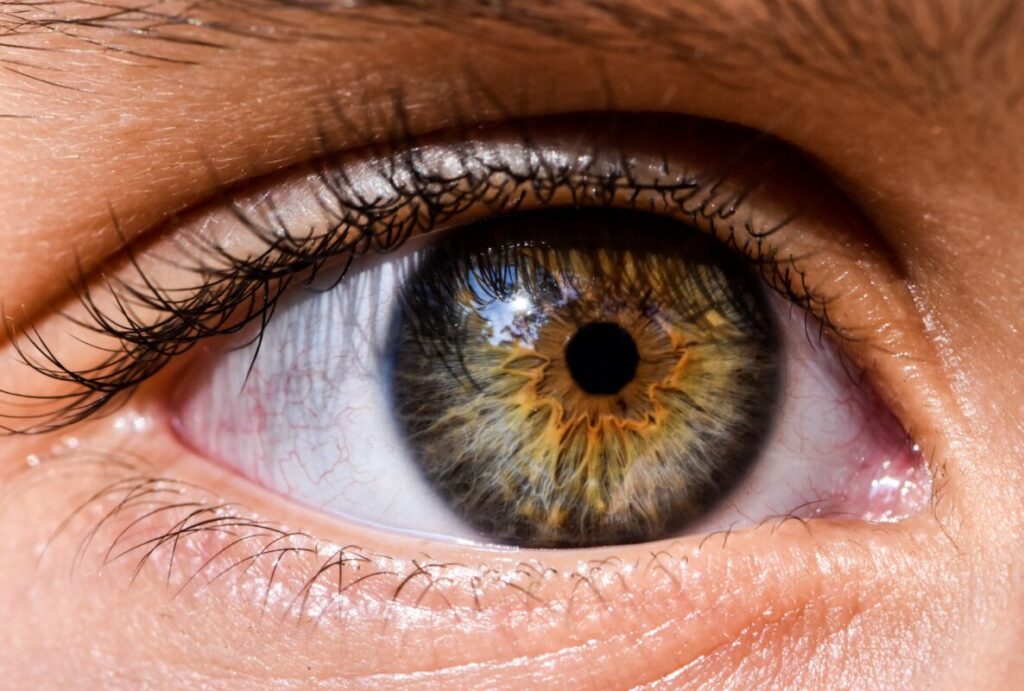
Mydriasis is the medical term for dilated pupils. It occurs when certain drugs stimulate the sympathetic nervous system, causing the muscles in the iris to contract and the pupils to enlarge. Stimulants like cocaine, amphetamines, and MDMA commonly cause this type of pupil dilation.
Anisocoria refers to a condition where one pupil is larger than the other. While this can occur naturally in some individuals, certain drugs like pilocarpine (used to treat glaucoma) or scopolamine (used to treat motion sickness) can cause uneven pupil dilation when administered or used recreationally.
Cycloplegia is a type of pupil dilation that occurs when drugs interfere with the eye’s ability to focus and constrict the pupil. This effect is often seen with anticholinergic drugs, such as atropine or diphenhydramine (found in some antihistamines), which can cause blurred vision, difficulty focusing, and pupil dilation.
While not a type of pupil dilation, Miosis (constricted pupils) can also occur due to drug use, particularly with opioids like heroin or morphine. In some cases, the presence of Miosis in a person with other symptoms of opioid use can help healthcare professionals identify and treat an overdose.
Stimulants
Stimulants are a class of drugs that increase activity in the central nervous system, leading to heightened alertness, increased energy, and elevated mood. Due to their stimulating effects, stimulants often cause pupil dilation.
Methamphetamine, or meth, is a powerful and addictive stimulant that significantly impacts the central nervous system. It causes a large dopamine release in the brain, leading to euphoria, increased energy, and alertness. Methamphetamine can cause mydriasis along with other side effects like dry mouth, sweating, and rapid heart rate.
Cocaine is a powerful central nervous system stimulant derived from coca plant leaves. It blocks the reuptake of dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin in the brain, increasing their levels and producing euphoria, increased energy, and heightened alertness. Cocaine can cause mydriasis, elevated heart rate, increased blood pressure, and constricted blood vessels as part of its stimulating effects.
Hallucinogens
Quick Tip
Be Aware of Drug Interactions
Can pupil dilation from drug use be dangerous?
How long does drug-induced pupil dilation last?
Can healthcare professionals tell if someone has used drugs based on their pupils?
Get Help for Substance Abuse at Cornerstone
We offer a wide range of treatment for mental health and substance abuse conditions. Begin your journey to recovery today!
Opiates and Opioids
Heroin is an illegal and highly addictive opioid derived from morphine, which comes from opium poppy plants. It is a potent analgesic that induces intense relaxation and euphoria. Although heroin typically causes pinpoint pupils (miosis), dilated pupils can occur during withdrawal or as a result of an overdose, which can lead to severe health consequences, including respiratory failure and death.
Recap of Drugs Causing Dilated Pupils
We’ve explored various drugs that can cause mydriasis or dilated pupils. These substances include:
- Stimulants like amphetamines, cocaine, and high doses of caffeine
- Hallucinogens such as LSD, psilocybin, mescaline, and DMT
- Opioids like heroin, morphine, oxycodone, and fentanyl in cases of overdose or withdrawal
The extent of pupil dilation and specific side effects experienced may vary depending on factors such as the type of drug, dosage, individual sensitivity, and duration of use.
Helping Someone with Suspected Drug Use
If you suspect someone you know may be under the influence of drugs due to dilated pupils, it’s essential to approach the situation with care and empathy. Your response can be critical in helping them seek support and preventing more severe consequences. Consider these steps:
- Observe and assess the situation: Take note of their behavior and other signs that might indicate drug use, like slurred speech, unsteady gait, or erratic behavior.
- Approach with care and empathy: Choose your words carefully and find a private, comfortable place to talk. Express your concern for their well-being and ask open-ended questions to encourage them to share their experience.
- Offer support and resources: If they admit to using drugs, offer your support and help them explore available resources like professional help, local support groups, mental health services, or addiction treatment programs.
- Recognize the limitations of your role: Understand that you cannot force someone to change their behavior or seek help if they are not ready. Provide support and encouragement, but know that your role is limited.
- Monitor the situation and prioritize safety: Call emergency services immediately if you believe they may be in immediate danger or suspect an overdose. Signs of potential overdose include extreme drowsiness, difficulty breathing, seizures, or loss of consciousness.
- Maintain communication and follow-up: Continue to check in with the person and offer your support. Keep an open line of communication and be available to listen, encourage, and share resources as needed.
Key Takeaways
- Key Takeaways
- Different drugs can cause distinct types of pupil dilation, such as mydriasis (stimulants), anisocoria (certain medications), cycloplegia (anticholinergics), and miosis (opioids).
- Pupil dilation caused by drug use can lead to various side effects, including increased sensitivity to light, blurred vision, and difficulty focusing. In some cases, prolonged dilation may result in more serious eye problems.
- While pupil dilation can be an indicator of drug use, healthcare professionals cannot definitively diagnose substance abuse based on pupil size alone. Other factors, such as medical conditions, brain injuries, and natural variations, must also be considered.
- Being aware of potential drug interactions is crucial when using prescription or over-the-counter medications, as some substances can affect pupil size when combined. Always consult with a healthcare provider or pharmacist to avoid potentially dangerous interactions.
How Drugs Affect Pupil Size
The impact of drug use on pupil dilation is a multifaceted issue. Different substances lead to unique changes in pupil size and function. From the widespread mydriasis caused by stimulants to the less common anisocoria induced by certain medications, these variations in pupil size can provide essential insights for healthcare professionals and concerned loved ones.
Pupil dilation is just one aspect of identifying drug use. While it can be a significant indicator, it must be considered with other symptoms and a thorough patient history to create a comprehensive understanding. By raising awareness about the dangers associated with drug use and the potential interactions between various substances, we can work together to create a safer, healthier community for all.
If you or someone close to you is grappling with substance abuse, know that you are not alone in this challenge. Cornerstone Healing Center offers compassionate, evidence-based care to help individuals overcome addiction and reclaim their lives. Our committed team of healthcare professionals supports you at every step of your journey, providing personalized treatment plans, a wide array of therapeutic approaches, and a judgment-free environment that places your well-being at the forefront. Remember that recovery is within reach, and we are here to guide you toward a brighter, drug-free future.